DON’T BE PANIC WHEN YOU RECEIVE A SCAM EMAIL FROM “YOURSELF”

1、Overview
Antiy CERT has recently received feedback from customers who received scam emails from themselves, extorting bitcoin. Analysis on this event revealed that it was a new fraud since October.
Since the sender address of the letterhead can be falsified arbitrarily, the fraudster falsified the sender’s email address to the victim’s email address, so that the victim could receive an email from himself, thereby the victim believed that his mailbox was hacked. Then, the fraudster claimed that the devices of victims had been installed with Trojans and had been under surveillance, intimidating the victims to send specified amount of money to a designated bitcoin account.
A large number of users on the Internet have reported receiving fraudulent emails using this type of method. Checking the bitcoin account reserved by the fraudsters, we can find that there are quite a large number of victims have been cheated and there are still victims who are transferring virtual currency to the fraudster’s account, with a total value of tens of thousands of dollars.
This type of scam email is simply a threatening and fraudulent mail that can be directly ignored and deleted, because the victim’s mailbox and devices are not hacked or controlled.
2、The Incident Analysis of Scam Email
The email was captioned: "The victim’s email address" + "was hacked," according to the scam email from user’s feedback. The titles of these kinds of emails basically include the following aspects:
1)It claims to be hackers from the "Dark Web" (such as fake ID, waite23/kurtis09/hugibert19/murry02), warning the victim “the email accounts have been stolen, please check to see if the recipients are victims themselves.
2)It shows that the victim’s machine has infected the Trojan injected by itself and has been monitored for a long time. The user’s online record and local data can be accessed at will, and the victim’s password change is no longer effective.
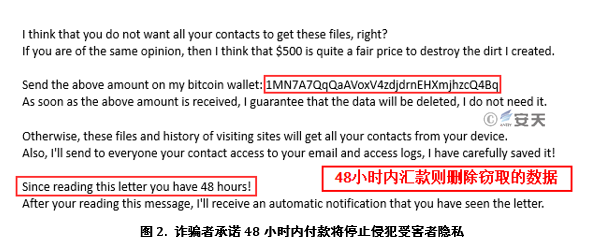
3)As long as the specified amount (such as $500) is remitted to the specified bitcoin address within 48 hours, the Trojan will be deleted and the attack will be stopped.
4)Some will continue to send emails and increase the amount.
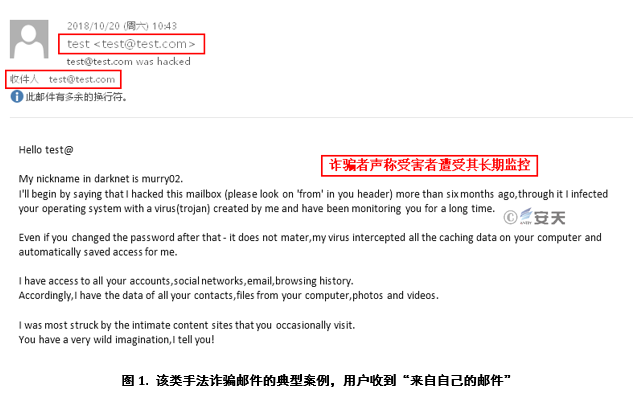
This is a typical Sextortion scam, which is a common type of online fraud. The fraudsters threatened the victim through a series of "evidence", such as "showing the account password that the victim had leaked," without invading the victim’s mailbox and equipment, saying “the mailbox had been stolen, the device was hacked by a real hacker”. Then they claimed to have been recording the screen and camera when the victim visited inappropriate content, such as an adult website. If the victim did not pay to the bitcoin wallet specified by the scammer, the matter would be made public.
The fraudulent means of proving that the victim’s mailbox has been stolen by a hacker by receiving “email form victims’ themselves” has emerged in recent times. If ordinary netizens do not know the fact that the letterhead of the mail can be arbitrarily forged, it is easy for the fraudster to deceive.
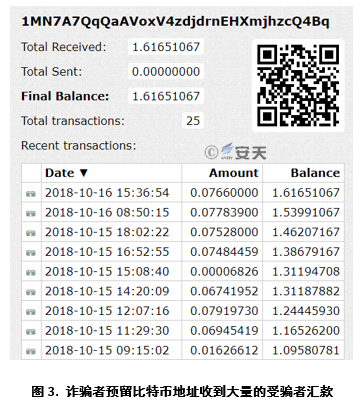
In our access to dozens of mail samples, the collection addresses selected by fraudsters are all Bitcoin wallet “1MN7A7QqQaAVoxV4zdjdrnEHXmjhzcQ4Bq”. Upon inquiry, it is learned that since October 13, 2018, the collection address has received 161,651,067 bitcoins remitted by the victim, which amounts to more than $10,000 at the current exchange price. Up to now, there are still victims making remittances to it.
The "from:" field can be arbitrarily modified to appear as any sender in the email because the header of SMTP protocol used for sending email can be constructed arbitrarily and some email service providers do not authenticate each other to forward email. However, for most mainstream email service providers (ESPs), such emails are actively blocked and filtered by the anti-spam function. Common email providers in the market support filtering of such spam, including direct rejection of the email.
Customers need to check whether the email system they are using is equipped with a spam filter or need to replace a more secure email system.
In addition, according to the data provided by BITCOINWHOSWHO,since September 2018, a large number of victims from 42 countries have claimed to have received scam emails similar to Sextortion using a variety of different methods. The report said that 621 bitcoin wallet addresses were collected, and the fraudsters received 540.27603,866 bitcoins in this extortion, which caused great economic losses to the victims.
3、Summary
In fact, this series of extortion emails is a blackmailer who spoofed the letterhead data and asked the victim to receive an "email from himself" to let the victim believe that his email box was compromised. However, in fact, the user’s email account and machine are not invaded and controlled by the fraudster, must not privately send money to the fraudster in case of fraud.
Although this type of extortion is not caused by the intrusion of the email, the email is still the most vulnerable to the attack. Following are advises for the users of the email and the email system maintainer:
Email security protection of user can refer to the following precautions:
1.Improve personal safety awareness. When we are sending and receiving emails, confirm whether the source is reliable. Do not click or copy the URLs in the emails. Do not easily download attachments from unknown sources. It is recommended that do not open emails from strangers.
2.Try not to log in to emails in an uncontrolled environment, such as computers in Internet cafes, computers of other people, etc.
3.Ensure the environmental security (PC, mobile phone, PAD, etc.) of the mail receiving and logging terminal system, timely update the vulnerability patch, install the terminal security protection software and upgrade and open the monitoring system in time to ensure the environment security of the mail sending and receiving.
4.The email password must use a strong password (for example, the password length is greater than 12 characters, and it must be a combination with number, English uppercase and lowercase letters, and special character), and the password should be changed periodically; the password must not be mixed with other services.
5.If using the mail client, please ensure the security of the client installation program, configure the mail sending and receiving according to the encrypted link mode (such as SSL) supported by the mail server, instead of using the plain text protocol to send and receive mail; for the volume of the mail client data file, Volume encryption (such as Bit locker) is recommended.
6.If you use a browser to send and receive mail, you need to use the HTTPS protocol to log in to the mailbox instead of using HTTP.
7.Sign the mail according to the organization’s rules.
8.Do not arbitrarily spread the email address, reduce the possibility of the attacker finding the attack portal; if you want to open the email address, you can replace the @ symbol with other symbols to avoid being crawled and recognized by the crawler and become the target of spam and attack mail.
To ensure security, the enterprise mail system requires a lot of related work. Here we give some references:
1. Improve personal safety awareness. When we are sending and receiving emails, confirm whether the source is reliable. Do not click or copy the URLs in the emails. Do not easily download attachments from unknown sources. It is recommended that do not open emails from strangers.
2. Secure the network security where the mail system is located: including network structure security, intrusion prevention, and security audit. For details, refer to Managed Network Plan V4.0 (NSA/IAD) .
3. Secure the security of the mail system: including the security policy of the server, operating system, and database. For details, refer to the DISA Security Technology Implementation Guide STIG.
4. Ensure the physical and management security of the mail system: including access control, management system, etc. For details, please refer to YD/T 3161-2016 Mail System Security Protection Requirements.
Appendix A. References
1.https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/security/email-security-appliance/whitepaper_C11-737596.html
2.https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/new-sextortion-scam-pretends-to-come-from-your-hacked-email-account/
3.https://bitcoinwhoswho.com/blog/2018/09/30/42-countries-report-sextortion-email-scam/
4.https://cryptome.org/2016/01/nsa-16-0114.pdf
5.https://iase.disa.mil/stigs/Pages/index.aspx#
